I’ll go over Is Crypto Prop Trading Legal in this post. Crypto prop trading enables traders to trade cryptocurrencies using the funds of a company.
Depending on local laws, license, and compliance, its legality differs between nations. To operate securely, stay out of trouble with the law, and maximize earnings while remaining completely compliance, traders must be aware of the regulations.
What is Crypto Prop Trading?
The practice of traders using a company’s capital instead of their own funds to trade cryptocurrencies is known as crypto proprietary (prop) trading. In this strategy, prop trading companies set risk limits, fund accounts, and frequently give the trader a cut of earnings.
Crypto prop trading, in contrast to retail trading, gives professional traders access to more capital and sophisticated tactics, allowing them to potentially generate substantial profits while controlling the firm’s risk. It has become more well-known as the cryptocurrency industry grows, providing chances for both experienced and novice traders.
Is Crypto Prop Trading Legal?

Depends on Jurisdiction
Different countries have different answers to how legally clear the regulations on crypto prop trading are for them. Some have laws regulating their crypto trading. Some of them have laws regulating portions of that. Some have no regulations at all for crypto trading. Some have no regulations at all for crypto trading.
Licensing Requirements
Some of the countries that have laws on the books regarding prop trading does require the prop trading companies to have a license or registration to be able to conduct business legally.
Regulated Platforms Only
If a licensed crypto prop trading company does not break the law, then their customers do not break the law by trading with them. Trading with a company that does not have a license is breaking the law in some countries, however.
Compliance Obligations
The company and the trader must follow KYC and AML regulations if they want to be law abiding.
Tax Reporting
If a trader makes a profit, they may need to report that profit and possibly pay a penalty if they do not, depending on the regulations in their country.
Risk of Enforcement
If a trader does business with a prop trading company, and that company does not have a business license, they are risking the prospect of being fined or having their account frozen or some other arrest related penalty.
How Crypto Trading Works
Funded Accounts
Prop trading firms give traders money to trade with rather than using their own. Firms place restrictions on how much can be traded.
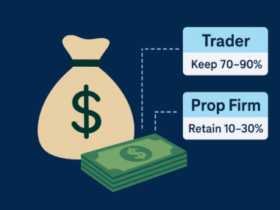
Profit Sharing
Traders get to keep a percentage of the profits they make off their trades while the firm keeps some as a fee for the provided trading capital.
Risk Management
To protect their investment, firms enforce the highest level of control on maximum daily losses, position sizes, stop-loss levels, and overall trading capital of the firm.
Trading Strategies
Firms have guidelines on how traders can make money. These can include strategies such as scalping, swing trading, or arbitrage.
Performance Evaluation
To keep receiving capital, firms expect the trader to be successful within the firm and obey the risk management rules consistently.
Leverage
Traders usually have more access to leverage than they would in retail trading which can increase profits as well as the risk.
Technology and Tools
Advanced trading software, analytics, and algorithmic trading tools are provided by the firms to help traders with their performance.
Key Regulatory Rules & Compliance
Licensing Requirements: Prop Trading Firm requires licencing from local financial authorities.
KYC (Know Your Customer): This requires verification of identity of the traders. This prevents fraudulent activities.
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) Compliance: Fraudulent activities are monitored by the firm’s system. Laundering of money is also monitored by the firm.
Securities & Derivatives Regulations: Some countries have an additional legal framework for the trading of Digital Currencies. This is because the crypto currencies for some countries are viewed as either securities or derivatives.
Tax Reporting Obligations: Every firm, as well as the traders are obligated to provide the authorities with their respective transactional activities.
Data Protection & Privacy Rules: Protection of the trader’s data must be secured by the firm.
Periodic Audits & Reporting: These activities of the firm may require Auditing, Reporting, or Disclosing.
Risks of Operating Without Legal Clarity
Fines and Penalties
Legal or financial repercussions could strike firms/traders based in unregulated areas.
Account Freezes or Asset Seizure
Funds can be confiscated, and trading accounts can be frozen if an authority deems the activities unlawful.
Reputation Damage
Non-compliance can be detrimental to the status of the traders and the prop trading companies.
Limited Legal Recourse
There is little to no legal protection for traders in the case of a conflict with unregulated firms or platforms.
Regulatory Crackdowns
Trading in a lawless area can leads to unannounced and sudden enforcement actions to stop trading on the platforms.
Financial Risk
Firms can go bankrupt or be the victims of scams, and traders can lose everything if no regulations apply to the trading platforms.
Tax Liabilities
Non-compliance to tax regulations can lead to penalties or even legal actions from the tax authorities.
Global Legal Landscape
| Region / Country | Legal Status | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Legal (regulated) | Must comply with SEC, CFTC, and state-level rules; licensed prop firms only. |
| European Union | Legal with regulations | MiCA regulations shaping clarity; KYC/AML compliance required. |
| United Kingdom | Legal (FCA-regulated) | Crypto derivatives and margin trading need authorization. |
| Japan | Legal (strict licensing) | FSA registration required; strong consumer protection rules. |
| Singapore | Legal (regulated) | MAS guidelines; licensed firms only. |
| South Korea | Legal (regulated) | Strict KYC/AML rules; only licensed firms operate legally. |
| Middle East (UAE, Bahrain) | Legal with framework | Licensed operations allowed; clear crypto frameworks in some countries. |
| Africa | Mostly unclear / restricted | Legal clarity varies; some countries developing crypto regulations. |
| Latin America (Brazil, Mexico) | Varies by country | Regulatory guidance exists in some countries; others remain unclear. |
| Offshore Platforms | Legal in some jurisdictions, risky elsewhere | Limited legal protection; compliance depends on offshore jurisdiction. |
Case Studies / Examples
Top Regulated Firms
Licensed trading firms such as B2C2 and FTX Prop Desk (prior to the collapse) integrated trading and compliance services.
Licensed UK Firms
UK-based CEX.IO and eToroX have prop trading for crypto under FCA guidelines, creating regulated, safe trading.
Platforms in Singapore
Singapore-based Genesis Trading is under MAS regulations, is one of the better examples of how important licensing is in the Asian market.
Examples of Enforcement
Some jurisdictions without any licenses had their accounts frozen and received fines, demonstrating the downside to being unregulated.
Success Stories
Using prop firms that are regulated allowed traders to achieve greater financial compliance, leverage, and profit potential.
Lessons Learned
The definition of regulations in any particular jurisdiction increases transparency, decreases the chances of legal issues for the trader, and decreases the risk to their capital.
Conclusion
Depending on the jurisdiction and the firm’s adherence to rules, cryptocurrency prop trading may be lawful.
Traders are required to disclose profits in accordance with local tax laws, use regulated platforms, and adhere to KYC/AML regulations. Both traders and businesses run the danger of fines, account freezes, and reputational damage when they operate in an unclear legal environment.
Traders can safely leverage capital, use cutting-edge tools, and optimize profit potential while remaining completely compliant by comprehending international legislation and selecting approved prop trading organizations.
FAQ
Crypto prop trading is when traders use a firm’s capital to trade cryptocurrencies, sharing profits with the firm while following risk rules.
No, legality varies by country. Some regions allow licensed firms, while others have restrictions or unclear regulations.
Traders themselves usually don’t need a license, but the prop trading firm must be properly licensed in its jurisdiction.
Risks include fines, account freezes, loss of funds, limited legal recourse, and reputational damage.
Use licensed platforms, follow KYC/AML rules, understand local regulations, and report profits for taxation.