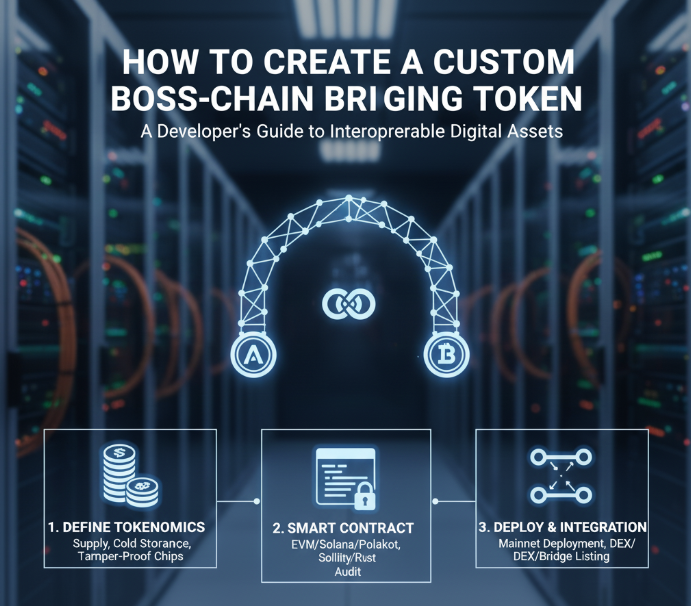
In this article, I will cover the How to Create a Custom Bridging Token, and I will break down the process into separate steps.
Everything will be covered. Everything from the design of the tokenomics and the creation of secure smart contracts to the mainnet deployment and integration with cross-chain circuits.
No matter whether it’s for DeFi, NFTs, or something else, you will be proficient in developing a secure and bridging token.
Understanding Bridging Tokens
Bridging tokens are a match for completing transactions on multiple blockchain networks by waling around a huge gap. To put it differently, it puts a representation of a token to work on a different blockchain.
Thus allowing for transactions for which only one kind of blockchain is used. For instance take a token on Ethereum, it can be bridged to Binance Smart Chain and it would still retain its value. However it would work with the new network.

Bridging tokens are one of the most important tokens used for cross-chain DeFi, NFTs and decentralized applications.
It promotes liquidity as well as interoperability. Bridging tokens use smart contracts and bridge protocols to do efficient transfers and secure transfers of multiple blockchains.
How to Create a Custom Bridging Token
Example: Creating a Custom Bridging Token
Step 1: Define Token Specifications
- Token details such as the token’s name, its symbol, its total supply and its decimals.
- For example:
- Name: BridgeToken,
- Symbol: BTK,
- Total Supply:1,000,000,
- Decimals: 18
Step 2: Choose a Blockchain Platform
- Choose the chain on which the token would exist for the token, for example, Ethereum, the Binance Smart Chain, and Polygon.
Step 3: Write Smart Contract
- For EVM chains, use Solidity, otherwise use the chains native language.
- Apply the ERC-20 standard functions such as transfer, approve, transfer From, balance Of and total Supply.
Step 4: Deploy the Token Contract
- A MetaMask wallet can be used to deploy through the Remix IDE or Hardhat.
- Contract verification is done through a block explorer.
Step 5: Integrate with a Bridge Protocol
- Select a bridging protocol, for example Allbridge or Snowbridge.
- Register the token on the bridge and create its wrapped version on the secondary chain.
Step 6: Test Cross-Chain Transfers
- Try sending a small amount of your token to the bridge and verify that it is properly placed on the other chain.
Step 7: Monitor & Launch
- Disseminate token details to users and check for issues related to the bridge activity.
- Manage the contract and modify bridge integrations as necessary.
Other Place Where to Create a Custom Bridging Token
Allbridge
Allbridge is a cross-chain token bridging protocol designed to provide a user friendly and efficient interface warp and transfer bridging tokens across different blockchains. Developers can deploy tokens on one network and immediately bridge across multiple networks, maintaining liquidity and cross-chain interoperability.

Unlike legacy bridges, Allblock focuses on custody and throughput while retaining low transaction costs, greatly focusing on value adds to DeFi, NFT and other multi-chain ecosystem integrations.
Allbridge’s intuitive dashboard and strong API support greatly lowers the technical entry barrier for cross-chain liquidation and cross network token management to smaller teams. By retaining the custody and transfer tokens on Allbridge, creators can easily preserve the value and reliability of custom bridging tokens across blockchains.
Multichain
Multichain focuses on making the process of creating, managing, and customizing bridging tokens on different blockchain networks easy.
With Multichain, developers can deploy a token on a blockchain and tether it to another, thus improving the interoperability and liquidity of DeFi, NFT, and multi-chain projects.
Multichain is particularly praised for its security, transaction speeds, and ease of use, making it a cross-chain solution for even the smallest teams.
With Multichain, creators of bridging tokens can maintain their value, reliability, and ease of use, as well as ensuring a seamless cross-network adoption and expansion to Multichain’s diverse ecosystems.
Best Practices for Custom Bridging Tokens
Conduct Security Audits
Smart contracts should be audited and assessed for potential exploits before deployment.
Use Established Libraries
Utilize reputable contracts and frameworks like Open Zeppelin for the ERC-20/ERC-721 standards.
Test on Testnets
Utilize test networks (Goerli, Ropsten) before the main net launch for deployment and token testing.
Set Clear Tokenomics
Ensure transparency and stability by defining the supply, distribution, and utility.
Monitor Bridge Activity
Track cross-chain transfers and monitor for abnormalities and other dependencies for lost transactions.
Implement Pause & Upgrade Functions
Emergency pause and upgrade functions can be done for added security.
User Education
Guides on bridging and token uses must be provided.
User Transparency
The community must be kept up-to-date on the latest changes, updates, audits, and other documented modifications.
Security Considerations
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Ensure contracts have no reentrancy or overflow issues and are free from other standard attacks.
Bridge Exploits
Losses on cross-chain transfers can be avoided if reputable and audited bridge protocols are used.
Private Key Management
Keep private keys in secure hardware wallets and other methods of storage.
Regular Audits
Audits on security conducted both before and after deployment should be thorough and professional.
Access Control
Restricting administrative control and applying multi signature wallets wherever practical.
Control Systems
Tokens and bridge transactions should be examined continuously and monitored for irregular behavior.
Emergency Mechanisms
Pause or upgrade functions should be available in case of malicious attempts to exploit a system.
Educated Users
Defining bridging as well as phishing attempts or other scams should be in the education system.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Enables cross-chain interoperability, allowing your token to move across multiple blockchains. | Smart contract development can be complex and prone to vulnerabilities if not audited. |
| Full control over tokenomics, supply, and features. | Requires technical expertise in Solidity and blockchain development. |
| Supports DeFi, NFTs, and cross-chain applications, expanding utility. | High deployment and gas fees, especially on mainnets like Ethereum. |
| Can increase liquidity and user engagement across chains. | Bridges can be targets for hacks or exploits if not properly secured. |
| Opportunity to innovate and create custom features tailored to your ecosystem. | Maintaining and monitoring the bridge and token requires ongoing resources. |
Conclusion
Designing a custom bridging token offers diverse channel monetization paths, a unique bridging liquidity approach, and versatile blockchain applications.
Defining the tokenomics model, executing smart contracts, and ensuring reliable bridging integrating process guarantee optimal bridging at all times. conducting audits, and best practices.
While challenges like technical complexity and prospective bridge risks are inevitable, well structured challenges mitigations will allow the custom bridging token to operate at max potential in the evolving multi-chain ecosystem.
FAQ
Yes, basic knowledge of Solidity, smart contracts, and blockchain development is required, though using templates like OpenZeppelin can simplify the process.
Absolutely. Always test on testnets like Goerli or Ropsten to verify functionality and prevent costly errors.
Conduct security audits, use reputable bridges, implement multi-signature wallets, and monitor transactions regularly.
Conduct security audits, use reputable bridges, implement multi-signature wallets, and monitor transactions regularly.