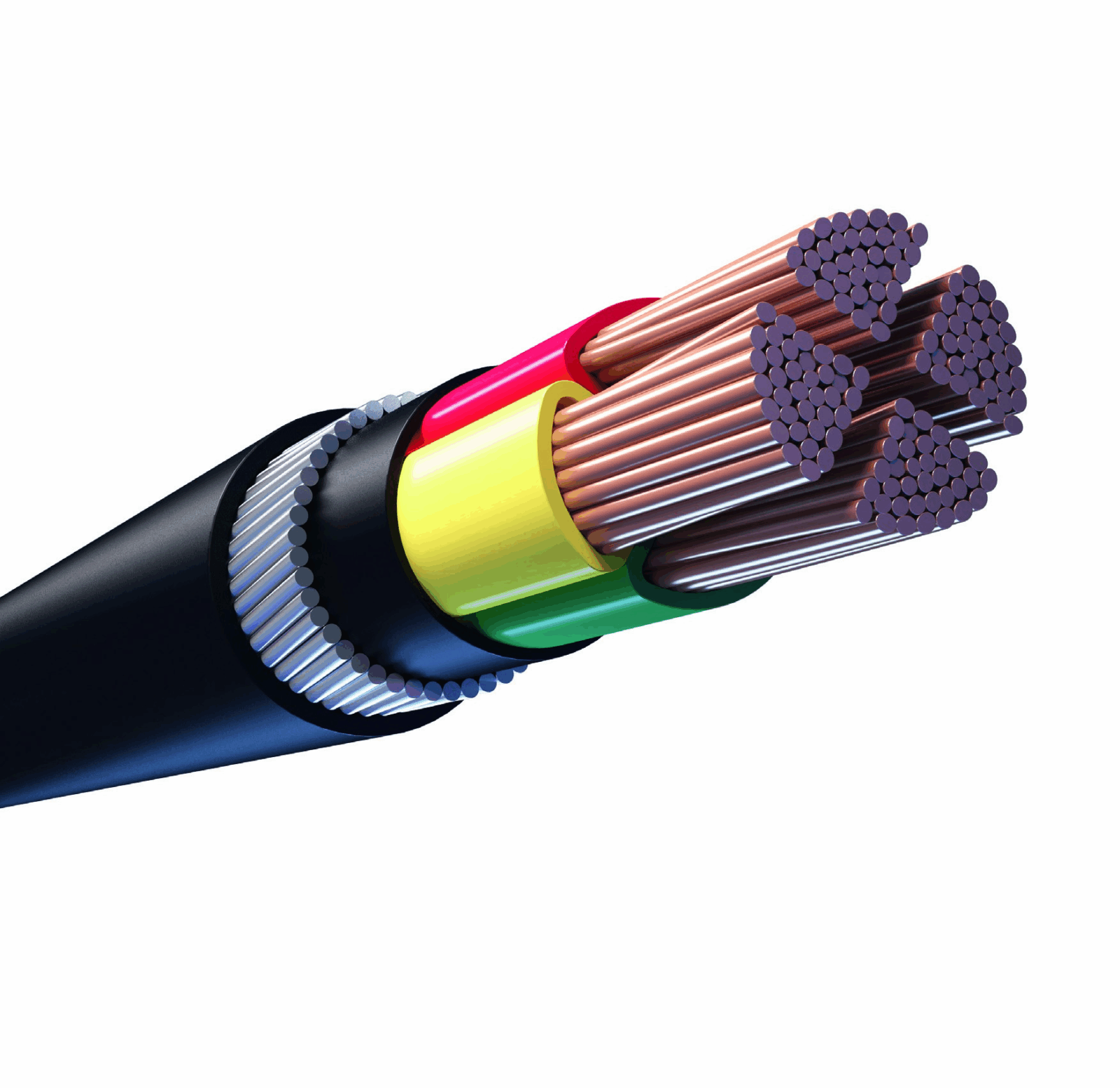
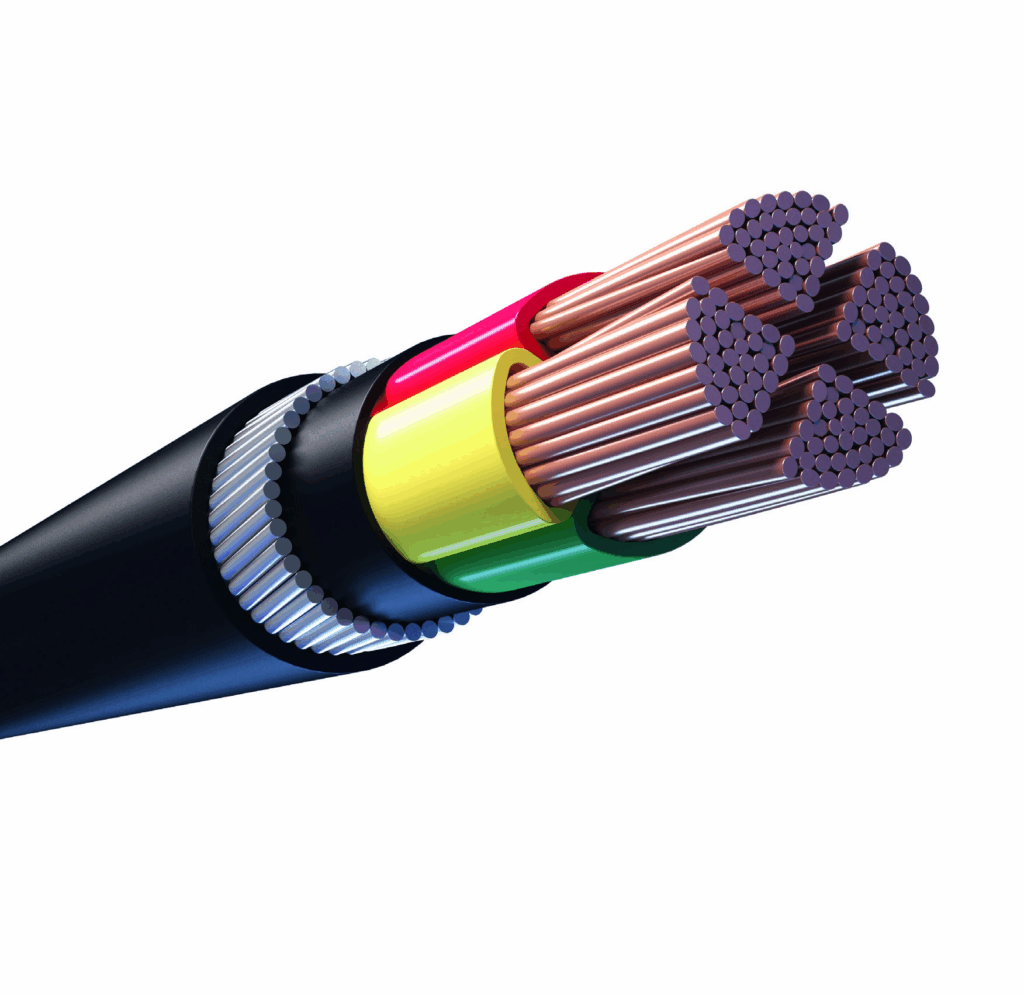
In this article, I will discuss the Why Use a Cable Cleat and discuss some of its key benefits in electrical systems.
Cable cleats are very important because they help in securing cable cleats; ensuring compliance and safety, and preventing damage during faults.
Knowing the role that cable cleats play in an industrial or commercial setting enhances reliability and mitigates maintenance issues in the long term.
What is a Cable Cleat?
A cable cleat serves the purpose of keeping electrical cables secured and supported, maintaining their position during both regular usage and in the event of faults. Like other cleats, they are made of metal, plastic, or composite materials.

Cable cleats are found in many settings, ranging from industrial installations to power plants. They mitigate short circuit damage, vibration damage, or damage from other external forces, preserving system safety and reliability. Installing cleats helps ensure compliance with legal and engineering standards.
Why Use a Cable Cleat
Short Circuit Protection
Protects cables from whipping and circuit damage during faults.
Improved Safety
Provides position securement which reduces fire and electric shock hazards.
Mechanical Support
Guards against strain, vibration, and external impacts on cables.
Reduce Cable Aging
Reduces the effects of aging, increasing reliability and durability.
Regulation
Fulfills requirements of international regulation IEC 61914.
Streamlined Maintenance
Organizes cables and reduces clutter to improve the ease of maintenance.
Key Benefits of Using Cable Cleats
Short-Circuit Restraint
Damage or dangerous movement is avoided as cable cleats secure cables during short-circuit incidents.
Enhanced Safety
Reduction in the risk of electrical fires, electric shock, and even cable entanglement is achieved through cable cleat restraining.
Mechanical Protection
They safeguard cables from physical strain, blows, and vibrations, particularly in industrial or outdoor environments.
Extended Cable Lifespan
Helps cables to be more functional and reliable by reducing wear and fatigue over time.
Regulatory Compliance
Installs are ensured to comply with standards IEC 61914 wiring systems which are mandatory in professional electrical systems.
Cable Congestion Reduction
Aesthetics improvement, maintenance simplification and inspection processes are enabled by the reduction of stray cables.
Simplified Categorization
Includes power plants, commercial facilities, and setups for renewable energy structures.
Applications of Cable Cleats
Power Generation Plants: Employed to anchor high-voltage cables in thermal, hydro, and nuclear plants where extreme short-circuit forces occur.
Industrial Facilities: Required in manufacturing plants, refineries, and vibrant factories wherein heavy industrial equipment is in constant operation.
Commercial Buildings: Safeguard and sustain the alignment of cables in large offices, malls, and other complexes with intricate electric networks.
Renewable Energy Systems: Used in wind farms and solar power plants for the administration and protection of power distribution cables.
Underground & Substation Installations: Restrains cable movement in confined high-load areas and prevents damage to cables.
Marine & Offshore Environments: Cleats that are resistant to corrosion serve for the management of cables on board ships, oil rigs, and in coastal installations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Insufficient Cleat Capacity
Selecting undersized cleats poses risks of cable damage and cleat failure from short-circuit impacts.
Setting Incorrect Spacing
Overly wide spacing between cleats reduces necessary support for the cable, increasing its movability.
Incompatible Materials Issue
Corrosion or damage to insulation can result from a mixture of materials, such as aluminum cables with metal cleats.
Ignoring Factors from Environment
Selecting cleats without resistance to moisture or chemical exposure risks premature wear.
Faulty Installation
Cables and the safety of the entire system can be jeopardized by loosely attached or misaligned cleats.
Non-adherence to Guidelines
Legal and operational risks are incurred from ignoring local guidelines and IEC 61914.
Risk & Considerations
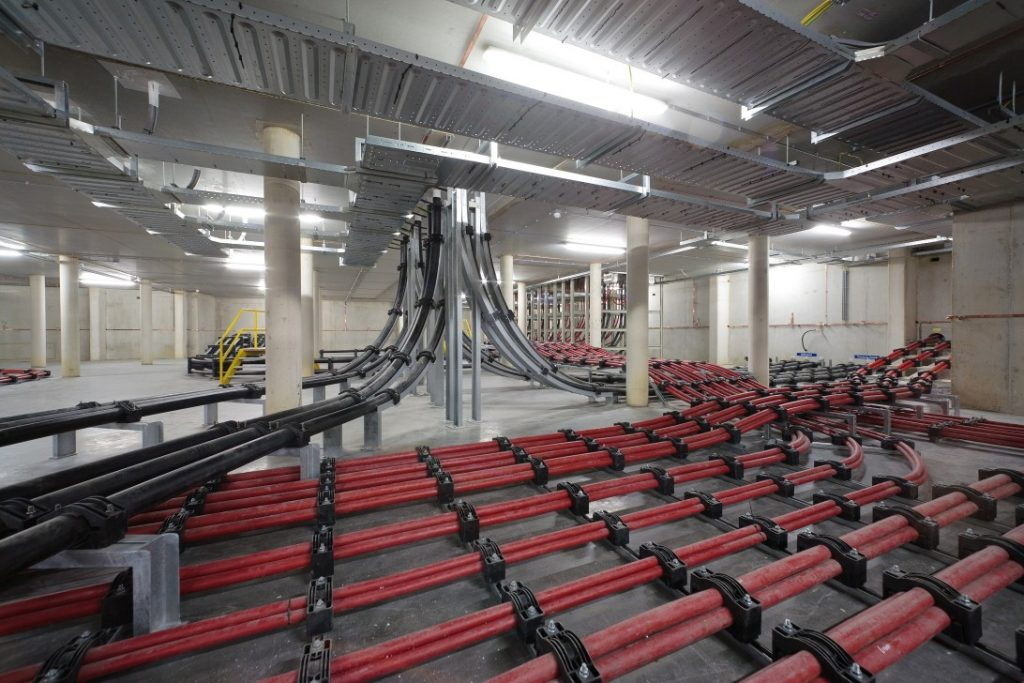

Inadequate Short-Circuit Protection: Not using high fault current rated cleats can lead to cable ejection and damage to systems during a short circuit.
Wrong Material Selection: Suitable materials may fail in harsh environments due to corrosion, chemical degradation, or other forms of premature failure.
Improper Spacing or Sizing: Wrong spacing of cleats or using the wrong size cleat for the cable can reduce effectiveness and compromise safety.
Environmental Exposure: Not considering temperature, UV, moisture, and chemicals, may weaken cleats over time.
Non-Compliance with Standards: Failure to adhere to international standards such as IEC 61914 can have legal, insurance, safety compliance or other risks.
Cost vs. Quality: Low cost lowers initial investment but increases risk of failures and associated maintenance costs.
Considerations
- Match cleat type with cable diameter and consider installation environment and mechanical load.
- Ensure installation is done by qualified installers.
- Purchase only after checking certification and performance documents for required ratings.
- Designs should comply with regulations, and layout and spacing should be determined by system design.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Provide secure cable support during faults | Improper installation can reduce effectiveness |
| Enhance electrical and fire safety | Higher initial cost compared to basic fixings |
| Extend cable lifespan by reducing stress | Material selection must match the environment |
| Ensure regulatory compliance (e.g., IEC 61914) | Requires careful planning and spacing |
| Improve cable management and organization | May need periodic inspection in critical systems |
| Suitable for various environments and setups | Incorrect sizing can lead to system failure |
Conclusion
Applying a cable cleat is critical for the safety, support, and durability of the electrical cable installation. It offers vital mechanical protection, prevents short-circuit damage, and aids in achieving international safety standards.
In an industrial, commercial, or renewable energy context, cable cleats mitigate risks, enhance cable longevity, and make maintenance easier. Choosing the appropriate cable cleat system is more than a technical decision; it secures dependable and safe electrical infrastructure.